This month, second graders learned about different types of texture art. We started off by working with a piece of clay and rolled it into a clay slab. Then we cut out our design and added texture on top. These came out very bright and beautiful, great work second graders!!
National
Visual Art Standards BY grade 4
1.1
Use a variety of materials and media, for example, crayons, chalk,
paint, clay, various kinds of papers, textiles, and yarns, and understand
how to use them to produce different visual effects
1.2
Create artwork in a variety of two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional
(3D)
media, for
example: 2D – drawing, painting, collage, printmaking, weaving; 3D – plastic
(malleable) materials such as clay and paper, wood, or found objects for assemblage
and construction
1.3
Learn and use appropriate vocabulary related to methods, materials, and
techniques
1.4
Learn to take care of materials and tools and to use them safely
2.1
For color, explore and experiment with the use of color in dry and wet
media
Identify
primary and secondary colors and gradations of black,
white and gray in the environment and artwork
Explore
how color can convey mood and emotion
For
example, students mix light and dark values of colors or predict the results of
overlapping and blending primary colors.
2.2
For line, explore the use of line in 2D and 3D works
Identify
a wide variety of types of lines in the environment and in artwork
For
example, students take a walk around the school and note jagged, straight,
curved, thick, and thin lines.
2.3
For texture, explore the use of textures in 2D and 3D works
Identify a wide variety of types of textures, for example, smooth, rough,
and bumpy, in the environment and in artwork
Create
representations of textures in drawings, paintings, rubbings, or relief
2.4
For shape and form, explore the use of shapes and forms in 2D and 3D
works
Identify
simple shapes of different sizes, for example, circles, squares, triangles, and
forms, for example, spheres, cones, cubes, in the environment and in
artwork
2.5
For pattern and symmetry, explore the use of patterns and symmetrical
shapes in 2D and 3D works
Identify
patterns and symmetrical forms and shapes in the environment and artwork.
Explain
and demonstrate ways in which patterns and symmetrical shapes
3.1
Create 2D and 3D artwork from direct observation
For
example, students draw a still life of flowers or fruit, action studies of
their classmates in sports poses, or sketches of the class pet having a snack
or a nap.
3.2
Create 2D and 3D expressive artwork that explores abstraction
For
example, a student simplifies an image by making decisions about essential
colors, lines, or textures.
3.3
Create 2D and 3D artwork from memory or imagination to tell a story or embody
an idea or fantasy
For
example, students draw members of a family from memory; illustrate a character
in a folktale or play; build a clay model of an ideal place to play; or make
images that convey ideas such as friendship.
4.1
Select a work or works created during the year and discuss them with a parent,
classmate, or teacher, explaining how the work was made, and why it was chosen
for discussion
For
example, a first grader chooses a painting and tells how she mixed the colors,
and talks about the decisions she made.
4.2
Select works for exhibition and work as a group to create a display
4.3
As a class, develop and use criteria for informal classroom discussions about
art
5.1
In the course of making and viewing art, learn ways of discussing it, such as
by making a list of all of the images seen in an artwork (visual inventory);
and identifying kinds of color, line, texture, shapes, and forms in the
work
5.2
Classify artworks into general categories, such as painting, printmaking,
collage, sculpture, pottery, textiles, architecture, photography, and film
5.3
Describe similarities and differences in works, and present personal responses
to the subject matter, materials, techniques, and use of design elements in
artworks
6.1
When viewing or listening to examples of visual arts, architecture, music,
dance, storytelling, and theatre, ask and answer questions such as, “What is
the artist trying to say?” “Who made this, and why?” “How does this work make
me feel?”
6.2
Investigate uses and meanings of examples of the arts in children’s daily
lives, homes, and communities
For
example, children learn and teach other children songs in languages other than
English; interview parents and community members about dances, songs, images,
and stories that are part of their family and cultural heritage.
7.1
Investigate how artists create their work; read about, view films about, or
interview artists such as choreographers, dancers, composers, singers,
instrumentalists, actors, storytellers, playwrights, illustrators, painters,
sculptors, craftspeople, or architects
For
example, teachers invite an illustrator of children’s books to school to show
how she creates her illustrations.











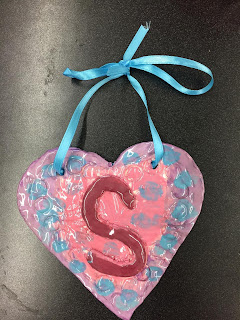





No comments:
Post a Comment